Step 1: Define Task and Outcome
Clearly articulate the specific task, desired result, and estimated completion time. Align expectations regarding deliverables and success criteria.
Mastering the 8 Steps of Delegation for Remote Team Member (RTM) Excellence and Reverse Delegation Strategies
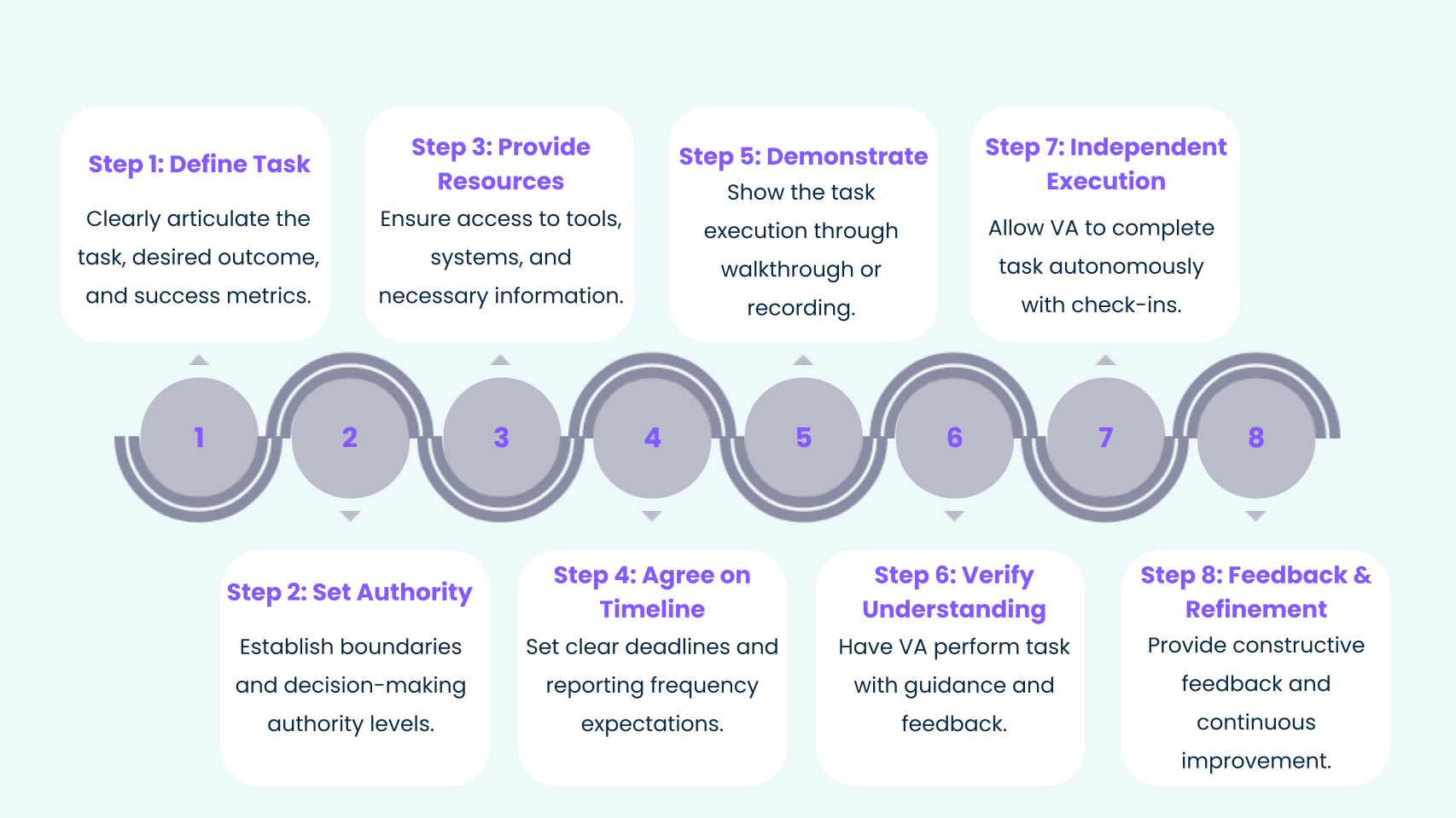
Clearly articulate the specific task, desired result, and estimated completion time. Align expectations regarding deliverables and success criteria.
Explicitly define the RTM's role and level of autonomy. Establish authority levels for tasks such as 'Do and Report' or 'Recommend and Act'.
Ensure the RTM has necessary credentials for tools, CRM access, and file-sharing systems. Provide background information and relevant documentation.
Define the frequency (daily/weekly) and format of progress updates. Establish transparent communication protocols and milestone checkpoints.
Lead by example by walking the RTM through the task from start to finish. Record the session to create a Standard Operating Procedure (SOP).
Shadow and support the RTM as they perform the task. Offer guidance, check back as needed, and ensure comprehension before proceeding.
Allow the RTM to complete the task alone, fostering initiative-taking and proactive management capabilities while remaining available for support.
Offer constructive feedback to refine performance until the RTM can complete the task accurately and efficiently without supervision.
.png)
Reverse delegation occurs when a RTM pushes tasks, decisions, or responsibilities back to the client instead of taking ownership and finding solutions independently.
Encourage RTMs to propose solutions alongside problems.
Establish when to escalate versus when to proceed independently.
Acknowledge and reward independent decision-making and initiative-taking.
.png?width=1706&height=959&name=test%20.pptx%20(3).png)
This principle reminds us that successful delegation extends beyond immediate task completion to building long-term VA capabilities, fostering independent decision-making, and creating scalable business operations that don't require constant supervision.